Yellow-billed Loon
General Description
The largest member of the loon family, the Yellow-billed Loon is larger and heavier than the Common Loon, which it resembles. Its creamy yellow bill is angled up at the end. Breeding and non-breeding plumages are similar to those of the Common Loon. The size and the yellow bill are the most reliable distinguishing features. In non-breeding plumage, identification is difficult. Consult a good field guide.
Habitat
Found farther north than the Common Loon, Yellow-billed Loons nest on large lakes in the high arctic tundra. In the winter, they spend time on coastal waters in bays and inlets, and among island groups.
Behavior
During the breeding season, Yellow-billed Loons are strongly territorial, excluding other loons and all other diving waterfowl from their territories. They form loose flocks during migration and occasionally on their wintering grounds.
Diet
Their diet is not well known, but most likely consists primarily of small to medium-sized fish, crustaceans, mollusks, and other aquatic creatures.
Nesting
The male appears to select the site, and both parents build the nest, a mound of muddy tundra vegetation with a depression at the center. Built on an island or on a mainland shore, the nest is partially hidden by surrounding vegetation and is often reused from year to year. The female lays two eggs, and both parents incubate. The young leave the nest one or two days after hatching and sometimes ride on their parents' backs. Both parents tend and feed the young and aggressively defend them.
Migration Status
Yellow-billed Loons migrate singly, in pairs, or in loose flocks. Mid-May to mid-June are the peaks of migration in the spring; fall peaks are from September to mid-October. They fly low over the water, along the coasts or up to more than a mile offshore.
Conservation Status
No conservation measures have yet been taken solely on behalf of this species. Yellow-billed Loons frequently drown in fishing nets and traps, and have been threatened by oil spills in their migratory and winter habitat. Disruption by oil field exploration and development are significant potential threats in their breeding habitat. Tundra habitat where Yellow-billed Loons breed is highly sensitive and slow to rebound to disturbance, so protection of this habitat is important to their population.
When and Where to Find in Washington
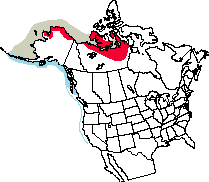
Yellow-billed Loons occur only in small numbers south of Canada. In Washington, they are rare winter residents on inland marine waters and occasionally on the coast. Within the last twenty years, they have been discovered wintering on large man-made reservoirs in eastern Washington. These recent reports are more likely due to better identification techniques rather than to an actual expansion of range.
 Abundance
Abundance
| Ecoregion | Jan | Feb | Mar | Apr | May | Jun | Jul | Aug | Sep | Oct | Nov | Dec |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Oceanic | ||||||||||||
| Pacific Northwest Coast | ||||||||||||
| Puget Trough | R | R | R | R | R | R | R | R | R | |||
| North Cascades | ||||||||||||
| West Cascades | ||||||||||||
| East Cascades | ||||||||||||
| Okanogan | ||||||||||||
| Canadian Rockies | ||||||||||||
| Blue Mountains | ||||||||||||
| Columbia Plateau |
Washington Range Map
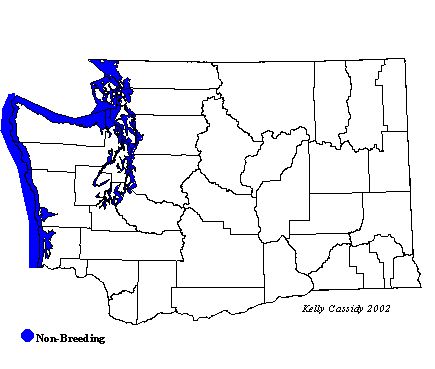
North American Range Map