Ross's Goose
General Description
The Ross' Goose is a small goose, similar in appearance to the Snow Goose. Like the Snow Goose, the Ross' Goose has a light and dark morph, although the dark-morph Ross' Goose is extremely rare. The light morph is white, and the dark morph is gray with a white head. Both morphs have black primaries. The bill is small and lacks the 'grin-patch' seen on the Snow Goose. Juveniles are mostly gray.
Habitat
The Arctic nesting grounds of the Ross' Goose, not discovered until 1938, consist of tundra, marshes, and ponds. In winter and during migration, these geese can be found in shallow lakes, fresh-water marshes, flooded fields, and other agricultural lands.
Behavior
Ross' Geese are usually in flocks, often mixed with Snow Geese. Their tendency to roost in tight flocks and be easily attracted to decoys may have made them vulnerable to market hunters, who had a significant impact on the population. These geese typically forage on the ground, wading or swimming in shallow water.
Diet
Almost exclusively plant-eaters, Ross' Geese eat grasses, sedges, and grain. In the fall, they eat more seeds and grains than grasses.
Nesting
Ross' Geese breed in colonies, starting in their second or third year. The nest is on an island or the shore of a tundra lake, often situated at the edge of a low thicket. The nest, built by the female after she lays her first egg, is a bulky pile of leaves, grass, and moss, depressed in the middle and lined with down. The female lays a total of 4 eggs and incubates them for about 3 weeks. The young leave the nest shortly after hatching. The parents lead the young to water and food, and the goslings feed themselves. The male stands guard and actively defends the young against predators. The young fledge at 40 to 45 days.
Migration Status
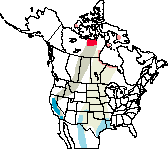
The vast majority of the population nests in the Queen Maud Gulf Migratory Bird Sanctuary in the central Canadian Arctic. They migrate to California's Central Valley, often in mixed flocks with other geese.
Conservation Status
The population of Ross' Geese was estimated at only 2,000 to 3,000 individuals in 1931. Protection from hunting has helped the Ross' Goose population recover to a 1988 total of 188,000 breeding birds, although it is still listed as a species-of-concern on the Partners in Flight watch list. Still on the increase, populations are now thought to be expanding their range greatly--birds have been found farther east and west in recent years during migration. Most nesting occurs within a refuge, and hunting is still prohibited, but loss of migration stopover and wintering habitat continues to threaten the Ross' Goose.
When and Where to Find in Washington
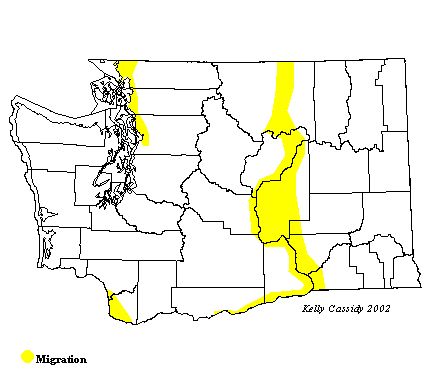
The Ross' Goose is a rare species, but is becoming more common in Washington. You may occasionally find it mixed in with Snow Geese or other mixed-species flocks in the winter in the lowlands on both sides of the Cascades, in both fresh- and saltwater habitats. Flocks of up to 30 Ross' Geese have become fairly regular in the spring and fall in far-eastern Washington.
 Abundance
Abundance
| Ecoregion | Jan | Feb | Mar | Apr | May | Jun | Jul | Aug | Sep | Oct | Nov | Dec |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Oceanic | ||||||||||||
| Pacific Northwest Coast | ||||||||||||
| Puget Trough | R | R | R | R | R | R | ||||||
| North Cascades | ||||||||||||
| West Cascades | ||||||||||||
| East Cascades | ||||||||||||
| Okanogan | R | R | R | R | ||||||||
| Canadian Rockies | R | R | R | R | ||||||||
| Blue Mountains | ||||||||||||
| Columbia Plateau | R | R | R |
Washington Range Map
North American Range Map

Family Members
 Fulvous Whistling-DuckDendrocygna bicolor
Fulvous Whistling-DuckDendrocygna bicolor Taiga Bean-GooseAnser fabalis
Taiga Bean-GooseAnser fabalis Greater White-fronted GooseAnser albifrons
Greater White-fronted GooseAnser albifrons Emperor GooseChen canagica
Emperor GooseChen canagica Snow GooseChen caerulescens
Snow GooseChen caerulescens Ross's GooseChen rossii
Ross's GooseChen rossii BrantBranta bernicla
BrantBranta bernicla Cackling GooseBranta hutchinsii
Cackling GooseBranta hutchinsii Canada GooseBranta canadensis
Canada GooseBranta canadensis Mute SwanCygnus olor
Mute SwanCygnus olor Trumpeter SwanCygnus buccinator
Trumpeter SwanCygnus buccinator Tundra SwanCygnus columbianus
Tundra SwanCygnus columbianus Wood DuckAix sponsa
Wood DuckAix sponsa GadwallAnas strepera
GadwallAnas strepera Falcated DuckAnas falcata
Falcated DuckAnas falcata Eurasian WigeonAnas penelope
Eurasian WigeonAnas penelope American WigeonAnas americana
American WigeonAnas americana American Black DuckAnas rubripes
American Black DuckAnas rubripes MallardAnas platyrhynchos
MallardAnas platyrhynchos Blue-winged TealAnas discors
Blue-winged TealAnas discors Cinnamon TealAnas cyanoptera
Cinnamon TealAnas cyanoptera Northern ShovelerAnas clypeata
Northern ShovelerAnas clypeata Northern PintailAnas acuta
Northern PintailAnas acuta GarganeyAnas querquedula
GarganeyAnas querquedula Baikal TealAnas formosa
Baikal TealAnas formosa Green-winged TealAnas crecca
Green-winged TealAnas crecca CanvasbackAythya valisineria
CanvasbackAythya valisineria RedheadAythya americana
RedheadAythya americana Ring-necked DuckAythya collaris
Ring-necked DuckAythya collaris Tufted DuckAythya fuligula
Tufted DuckAythya fuligula Greater ScaupAythya marila
Greater ScaupAythya marila Lesser ScaupAythya affinis
Lesser ScaupAythya affinis Steller's EiderPolysticta stelleri
Steller's EiderPolysticta stelleri King EiderSomateria spectabilis
King EiderSomateria spectabilis Common EiderSomateria mollissima
Common EiderSomateria mollissima Harlequin DuckHistrionicus histrionicus
Harlequin DuckHistrionicus histrionicus Surf ScoterMelanitta perspicillata
Surf ScoterMelanitta perspicillata White-winged ScoterMelanitta fusca
White-winged ScoterMelanitta fusca Black ScoterMelanitta nigra
Black ScoterMelanitta nigra Long-tailed DuckClangula hyemalis
Long-tailed DuckClangula hyemalis BuffleheadBucephala albeola
BuffleheadBucephala albeola Common GoldeneyeBucephala clangula
Common GoldeneyeBucephala clangula Barrow's GoldeneyeBucephala islandica
Barrow's GoldeneyeBucephala islandica SmewMergellus albellus
SmewMergellus albellus Hooded MerganserLophodytes cucullatus
Hooded MerganserLophodytes cucullatus Common MerganserMergus merganser
Common MerganserMergus merganser Red-breasted MerganserMergus serrator
Red-breasted MerganserMergus serrator Ruddy DuckOxyura jamaicensis
Ruddy DuckOxyura jamaicensis

